Side Effect: Anxiety
What is Anxiety?
Anxiety is a common mental health condition characterized by persistent and excessive worry or fear in response to different stimuli or situations. It is normal to feel anxious periodically, but when anxiety becomes very severe, present in almost every aspect of daily life, lasts for an extended period of time, or significantly decreases your quality of life, then anxiety can be considered a medical problem.
What does Anxiety look like?
Anxiety can manifest itself in a variety of ways, but is often classified as either 1) general anxiety disorder (GAD) or 2) panic disorder (PD). GAD typically consists of constant and excessive worry about day-to-day situations, while PD consists of recurrent and unexpected panic attacks and surges of fear that often occur without a clear trigger. Some symptoms of each type of anxiety include:
General Anxiety Disorder
- Feelings of worry and fear
- Restlessness
- Fatigue
- Trouble concentrating
- Irritable
- Trouble sleeping
- Muscle tension
Panic Disorder
- Fast heartbeat
- Sweating
- Shortness of breath
- Shaking
- Nausea
- Chest pain
- Dizziness
- Loss of control
Anxiety
Click to enlarge
If not adequately controlled, anxiety can interfere with many aspects of your life. It is important to speak with your doctor about any anxiety symptoms you are having. Your doctor will want to know if you are having anxiety and they may have ideas to help you control it.
Who gets Anxiety?
Anxiety can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or background. Is estimated that almost 5% of the global population is affected by anxiety, and the true number of those affected over an individual’s lifetime is likely much higher. Importantly, approximately 12-25% (as many as 1 out of every 4) people with cancer suffer from anxiety.
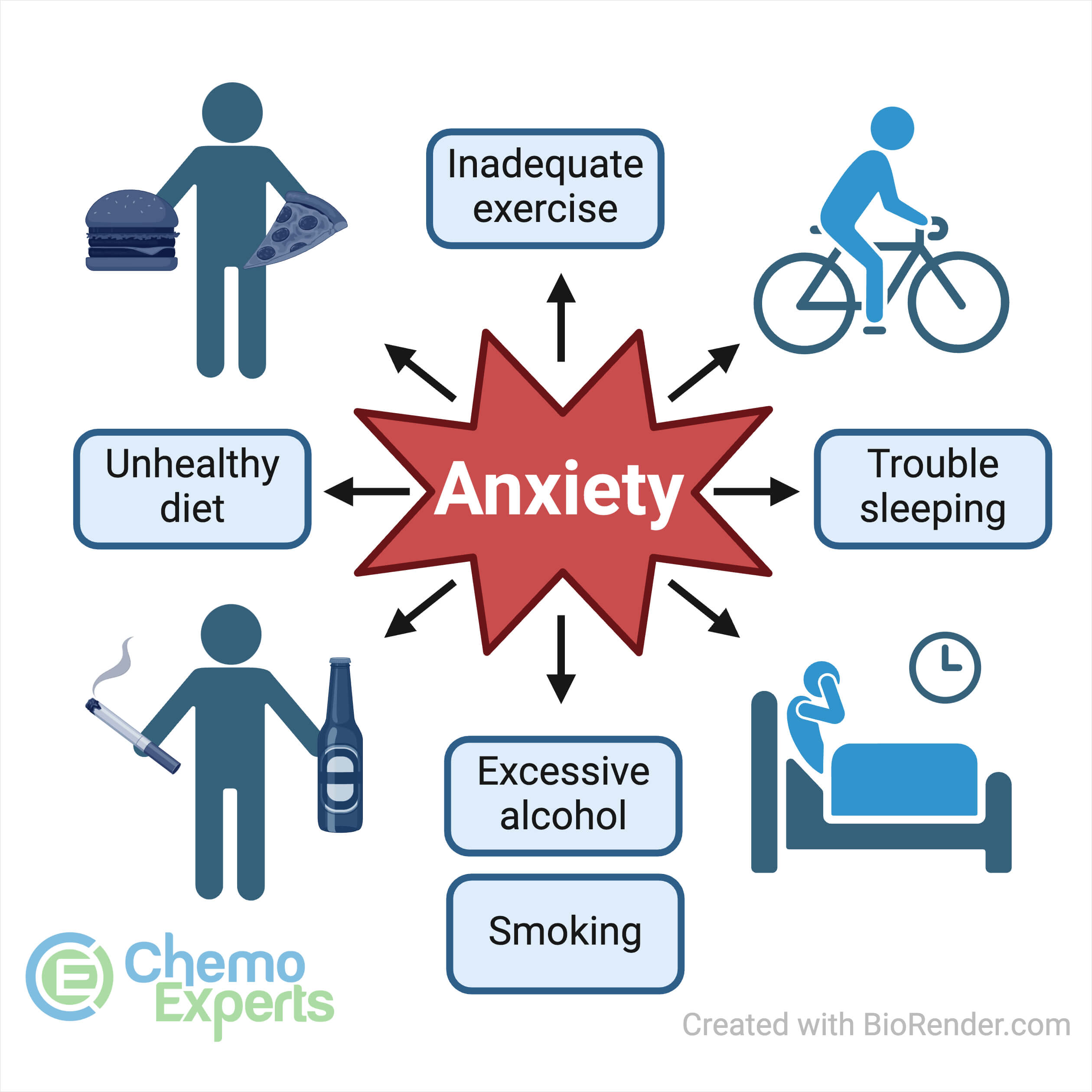
Factors that can worsen anxiety symptoms include receiving a life-threatening cancer diagnosis, having more advanced stage of disease, unemployment, younger age, having bothersome symptoms, receiving intensive treatment, poor social functioning or not having support, and poor communication with healthcare providers.
How to prevent Anxiety
Strategies to prevent anxiety include practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga, getting regular exercise, maintaining a healthy diet, and seeking support from family and friends.
How to treat Anxiety
When it comes to treating anxiety in cancer patients, there are different approaches depending on the severity of the symptoms and the patient's overall health.
A support group is a good, non-medication way to learn more about anxiety and develop skills to help you deal with it. If effective, medications (which may have side effects) may not be needed. Other commonly used, therapies include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), mindfulness-based therapy (MBT).
Non-pharmacologic based therapy may be enough alone to treat patients with mild or moderate symptoms of anxiety where more severe cases typically necessitate the addition of pharmacologic therapy. So, if the strategies above do not help as much as you were hoping, medications such as antidepressants and anxiolytics may be prescribed by your doctor. Some commonly used medications to treat anxiety include:
Benzodiazepines
- Alprazolam (Xanax®)
- Lorazepam (Ativan®)
- Diazepam (Valium®)
- Clonazepam (Klonopin®)
Antidepressants
- Fluoxetine (Prozac®)
- Citalopram (Celexa®)
- Escitalopram (Lexapro®)
- Paroxetine (Paxil®)
- Sertraline (Zoloft®)
- Duloxetine (Cymbalta®)
- Venlafaxine (Effexor®)
- Bupropion (Buspar®)
- Mirtazapine (Remeron®)
Other classes:
Created: March 4, 2024
Updated: March 4, 2024

